Home Telephone Amplifier Circuit
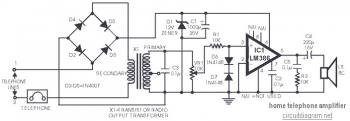
Here the home telephone amplifier circuit schematic:
This circuit can be build and tested with ease. There is no extra electrical power supply necessary to power up the telephone amplifier circuit, as it draws power from the telephone line itself. The amplifier will give fairly excellent volume for the telephone conversation to be properly heard in a living room.
A volume control for this telephone amplifier is included to adjust the volume as desired. The circuit is built around IC LM386. Diodes D6 and D7 are put to use to limit the input signal strength. Transformer X1 can be a transistor radio’s output transformer utilised in reverse. As original secondary (output) winding is connected in series with the telephone lines, the speech signals passing via the lines make alteration within the magnetic flux within the core of transformer and thereby induce signal voltage across the main winding. This audio signal is used as input for IC LM386. Diodes D2 through D5 connected in bridge configuration constitute a polarity guard to ensure that the amplifier is powered with correct polarity, irrespective of the line polarity, Zener diode D1 may possibly have any breakdown voltage between 6 and 12 volts range.
There's no will need of a separate power switch as the circuit energises (via the typically open contacts of the cradle switch) when one lifts the handset. The circuit may well be wired on a general-purpose PCB or by etching a PCB for this circuit. The circuit can be simply tested by connecting a 6 volts supply to line terminals 1 and 2. A hissing sound is going to be heard from the loudspeaker. Now connect 6V AC from a transformer to terminals 1 and 2 and observe hum within the loudspeaker. The volume of the hum can be changed through potentiometer VR1. Diodes D6 and D7 limit the input below ± 700 mV. The circuit would be to be connected to the telephone lines in series with the telephone instrument, as shown in the figure.
Home Telephone Amplifier Circuit
About Audio Amplifier
An audio amplifier is an electronic amplifier that amplifies low-power audio signals (signals composed primarily of frequencies between 20 - 20 000 Hz, the human range of hearing) to a level suitable for driving loudspeakers and is the final stage in a typical audio playback chain.
The preceding stages in such a chain are low power audio amplifiers which perform tasks like pre-amplification, equalization, tone control, mixing/effects, or audio sources like record players, CD players, and cassette players. Most audio amplifiers require these low-level inputs to adhere to line levels.
While the input signal to an audio amplifier may measure only a few hundred microwatts, its output may be tens, hundreds, or thousands of watts. More explanation about power audio amplifier can be found at wikipedia.org
An audio amplifier is an electronic amplifier that amplifies low-power audio signals (signals composed primarily of frequencies between 20 - 20 000 Hz, the human range of hearing) to a level suitable for driving loudspeakers and is the final stage in a typical audio playback chain.
The preceding stages in such a chain are low power audio amplifiers which perform tasks like pre-amplification, equalization, tone control, mixing/effects, or audio sources like record players, CD players, and cassette players. Most audio amplifiers require these low-level inputs to adhere to line levels.
While the input signal to an audio amplifier may measure only a few hundred microwatts, its output may be tens, hundreds, or thousands of watts. More explanation about power audio amplifier can be found at wikipedia.org

0 comments:
Post a Comment